JavaScript’s built-in functions are your Swiss Army knife for daily coding tasks and technical interviews. Beyond the basics, here are some powerful functions with real-world applications.

Math
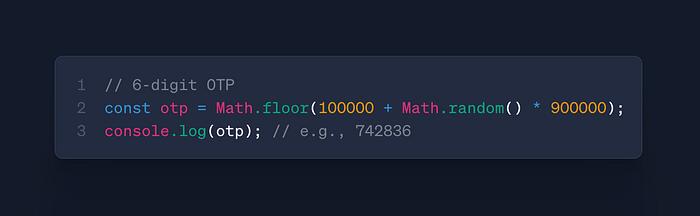
Math.random()
- Use: Generate random numbers
- Case: OTP generation, random sampling
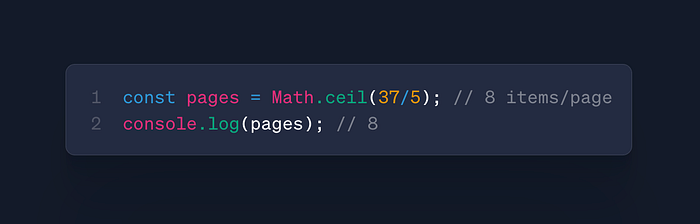
Math.floor() vs Math.ceil()
- Use: Precise number handling
- Case: Pagination, financial calculations
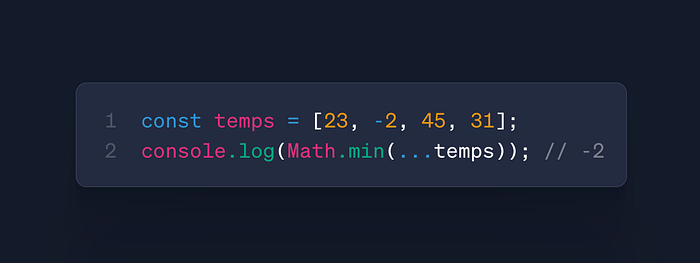
Math.max()/Math.min()
- Use: Find extremes in datasets
- Case: Data analysis, validation
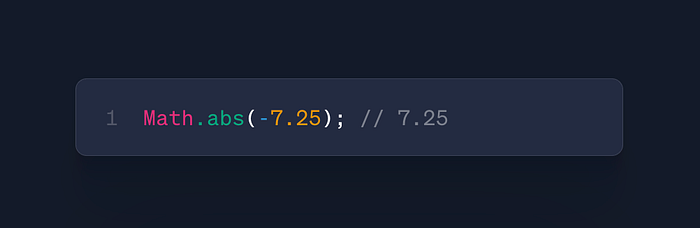
Math.abs(x)
- Use: Absolute value
- Case: Distance calculations, input validation
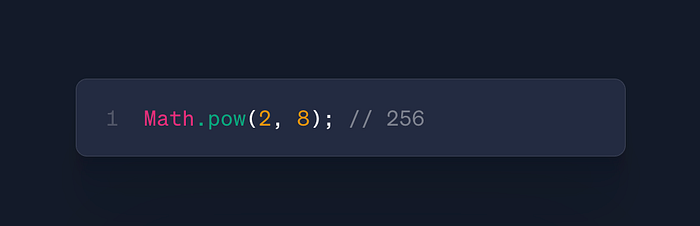
Math.pow(base, exponent)
- Use: Exponentiation
- Case: Compound interest, animation curves
Advanced String Magic
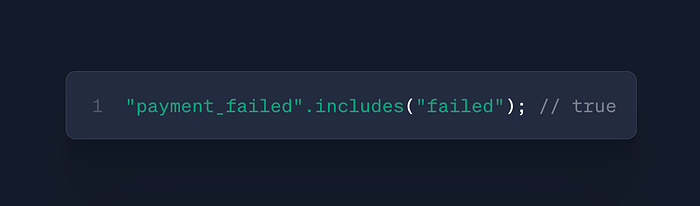
str.includes()
- Use: Substring detection
- Case: Search features, content filtering
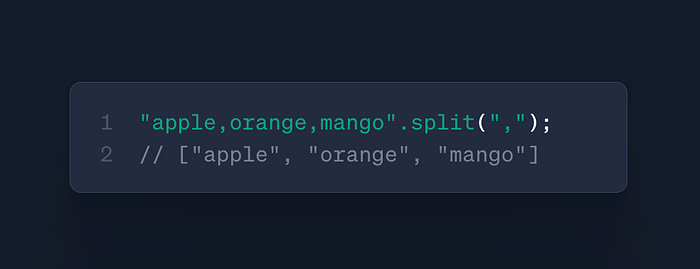
str.split()
- Use: String → Array conversion
- Case: CSV parsing, text processing
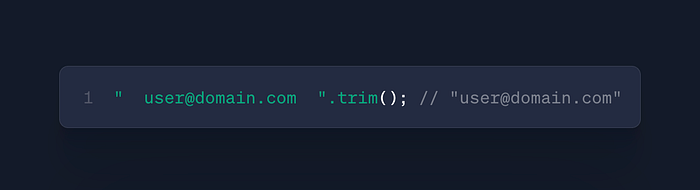
str.trim()
- Use: Remove whitespace
- Case: Form input sanitization
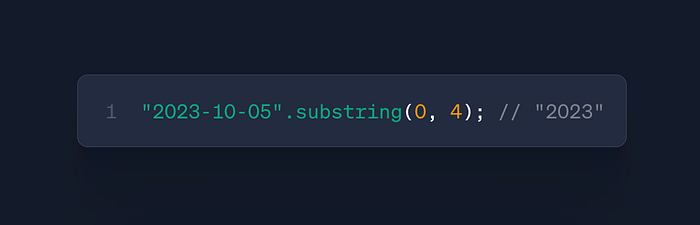
str.substring(start, end)
- Use: Extract substring between indices
- Case: Truncating text, parsing IDs
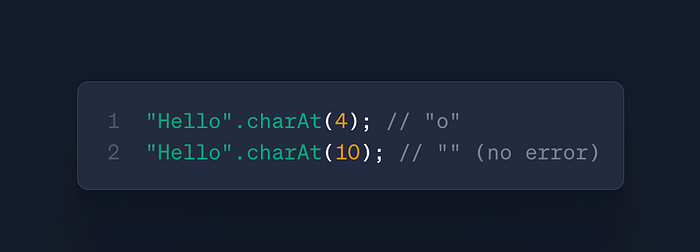
str.charAt(index)
- Use: Safe character access (vs
str[index]in older JS) - Case: Password validators, string analysis
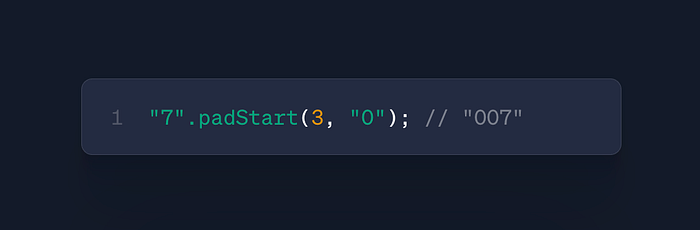
str.padStart(length, padding)
- Use: Format strings to fixed length
- Case: Display IDs, financial formatting
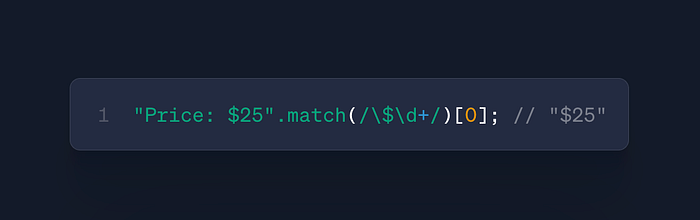
str.match(regex)
- Use: Extract patterns with regex
- Case: Data scraping, validation
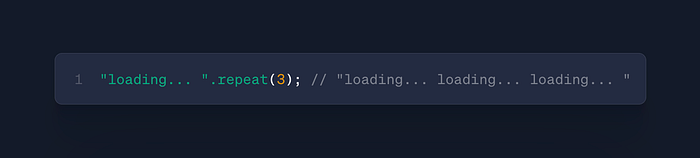
str.repeat(count)
- Use: Create repeated strings
- Case: Loading animations, text formatting
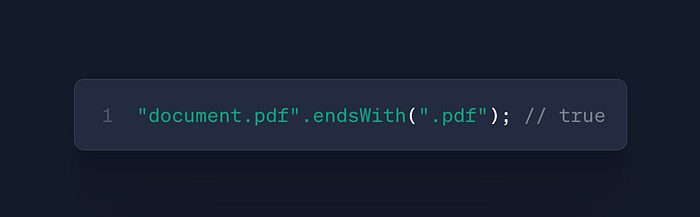
str.endsWith(searchString)
- Use: Suffix verification
- Case: File type validation
Advanced Array Techniques
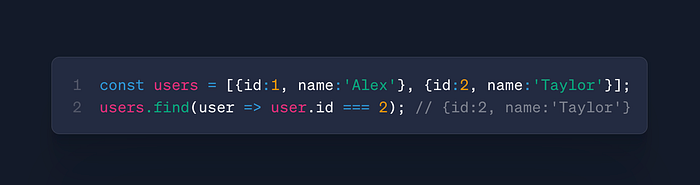
arr.find()
- Use: Find first match
- Case: User lookup, inventory search
arr.some()/arr.every()
- Use: Conditional checks
- Case: Permissions, validation

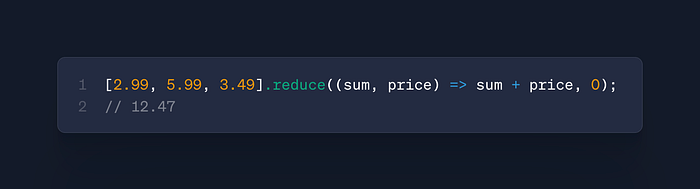
arr.reduce()
- Use: Accumulate values
- Case: Shopping carts, data aggregation
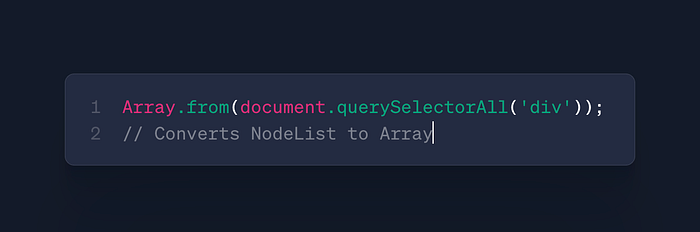
Array.from()
- Use: Convert array-likes to arrays
- Case: DOM manipulation, arguments handling
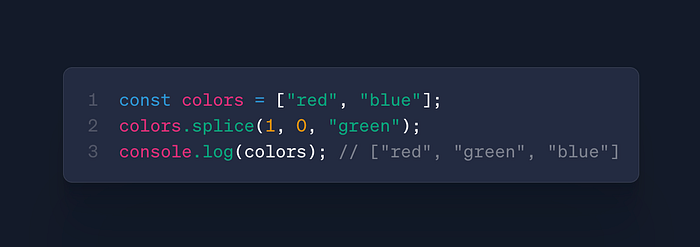
arr.splice(start, deleteCount, ...items)
- Use: Insert/remove elements at any position
- Case: Dynamic lists, reordering
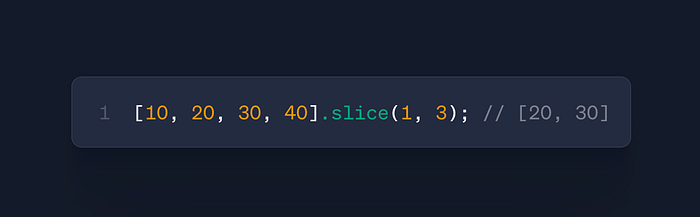
arr.slice(start, end)
- Use: Create shallow copies of array segments
- Case: Pagination, undo/redo features
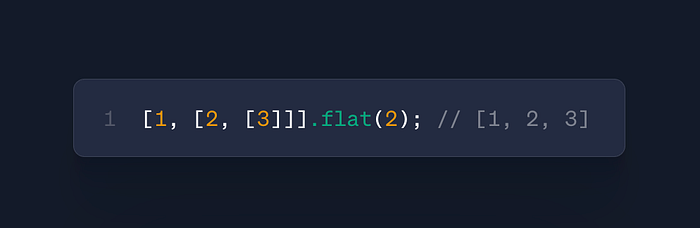
arr.flat(depth)
- Use: Flatten nested arrays
- Case: API response normalization
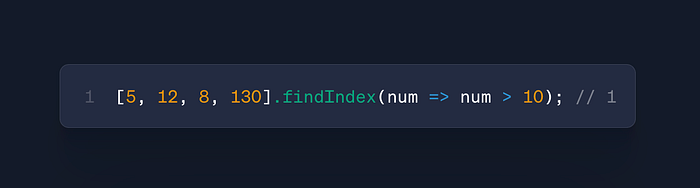
arr.findIndex(callback)
- Use: Find position of first matching element
- Case: Bulk operations, data indexing
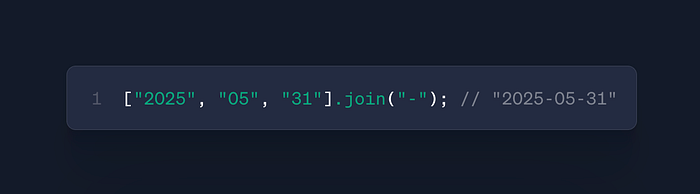
arr.join(separator)
- Use: Convert array → string with custom separator
- Case: CSV generation, URL parameters
arr.reverse()
- Use: Reverse element order
- Case: UI rendering (newest first), palindrome checks

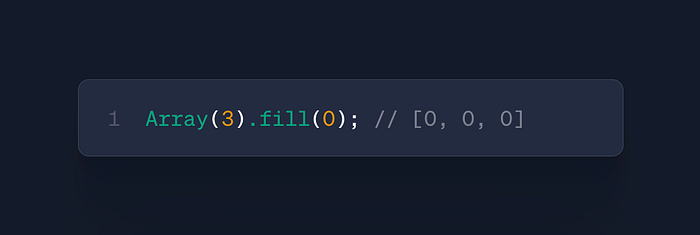
arr.fill(value, start, end)
- Use: Initialize arrays with default values
- Case: Matrix creation, reset operations
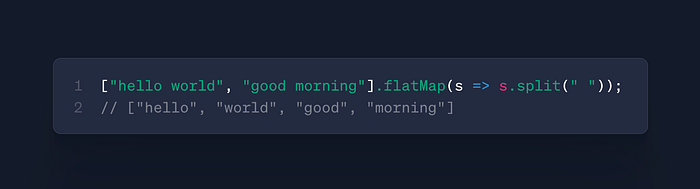
arr.flatMap(callback)
- Use: Map + flatten in single operation
- Case: Data normalization, tag processing
Date Manipulation
Date.parse()
- Use: Convert string → timestamp
- Case: Time calculations, countdowns
new Date() Constructor
- Use: Create date objects from various inputs
- Case: User input handling, timestamp conversion
date.getFullYear()/date.getMonth()/date.getDate()
- Use: Extract date components
- Case: Age calculation, date formatting
date.setFullYear()/date.setMonth()
- Use: Modify date components
- Case: Subscription renewals, date arithmetic
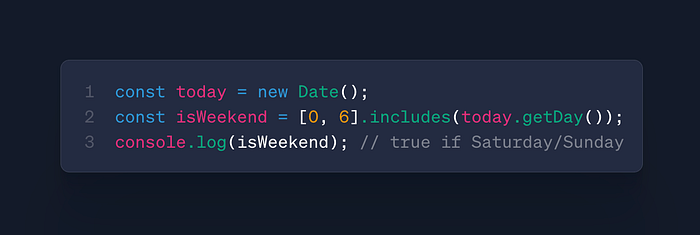
date.getDay()
- Use: Get weekday index (0=Sunday)
- Case: Scheduling, business day calculations
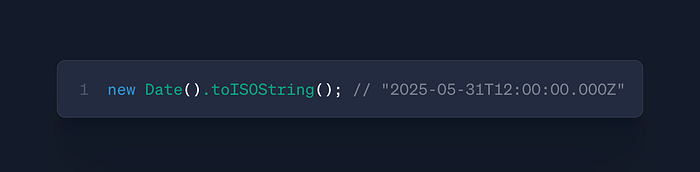
date.toISOString()
- Use: Convert to ISO 8601 format
- Case: API payloads, database storage
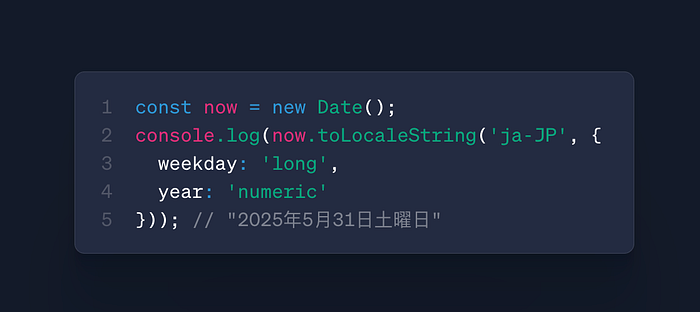
date.toLocaleString(locale, options)
- Use: Fully localized date/time formatting
- Case: International applications
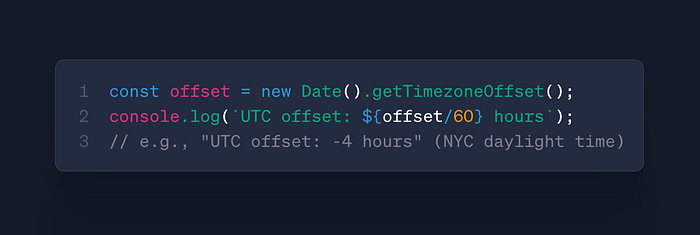
date.getTimezoneOffset()
- Use: Get UTC offset in minutes
- Case: Timezone conversions
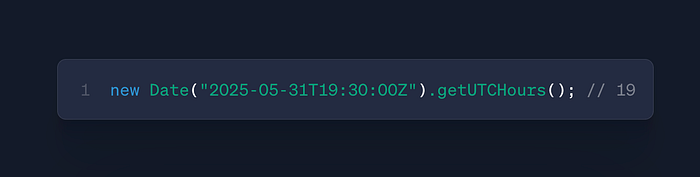
date.getUTCHours()
- Use: Get UTC hour (0–23)
- Case: Global scheduling systems
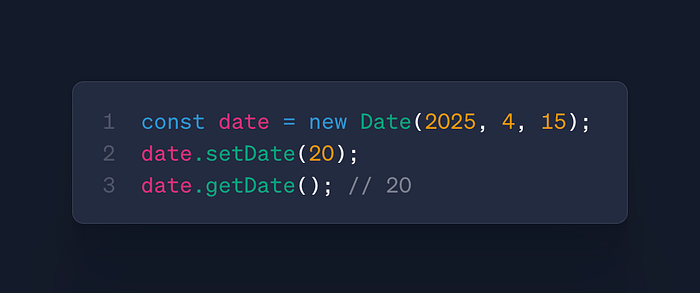
date.setDate(day)
- Use: Set day of month (1–31)
- Case: Calendar navigation, due date calculation
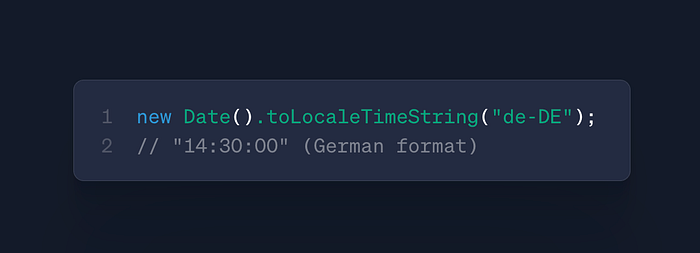
date.toLocaleTimeString()
- Use: Culture-sensitive time formatting
- Case: Localized dashboards
Utility Power Tools
- Case: User input handling, timestamp conversion
Utility Power Tools
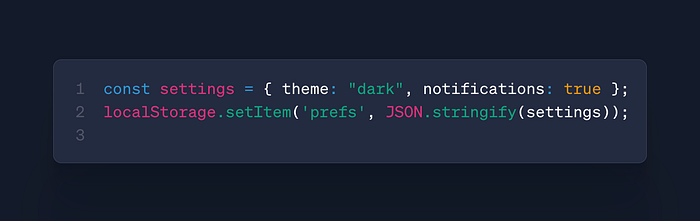
JSON.parse()/JSON.stringify()
- Use: Data serialization
Object.keys()/Object.values()
- Use: Object introspection
- Case: Dynamic forms, configuration
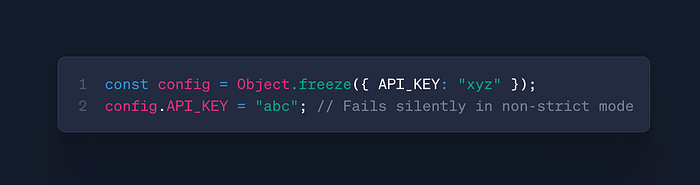
Object.freeze(obj)
- Use: Make object immutable
- Case: Configuration objects, constants
Number.toFixed(digits)
- Use: Fixed-point notation
- Case: Currency formatting, measurements

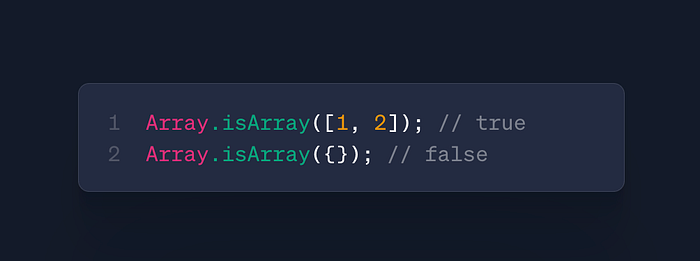
Array.isArray(value)
- Use: Type checking for arrays
- Case: API response validation
Conclusion
These functions represent the core toolkit I’ve relied on throughout my career for real-world JavaScript challenges, interviews, and projects. While no one needs to memorize them all in the age of AI, having this mental index helps tremendously when you’re stuck designing complex logic during coding challenges or debugging sessions. Keep this reference handy — not as a study guide, but as a practical map to navigate JavaScript’s built-in capabilities efficiently when tackling tough problems.
When in doubt: Combine simple functions instead of writing complex code.
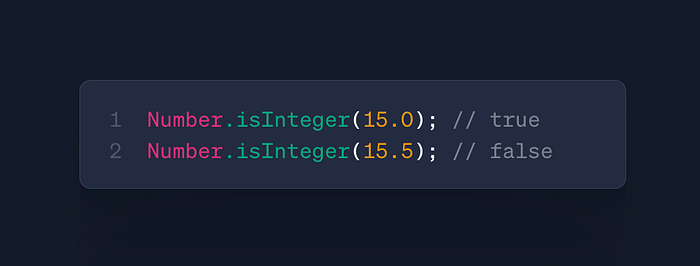
Number.isInteger()
- Use: Validate numbers
- Case: Input validation, type checking
Comments
Post a Comment